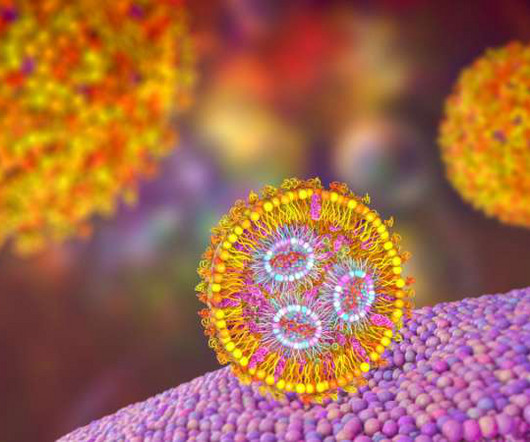
LNP formulations produce strong immune responses, data shows
Drug Discovery World
FEBRUARY 15, 2024
The etherna paradigm for cLNP design is ushering in the rapid generation of novel families of delivery systems for not only vaccination but also for in vivo tolerisation for a host of autoimmune diseases.” The post LNP formulations produce strong immune responses, data shows appeared first on Drug Discovery World (DDW).








Let's personalize your content