SSRgenotyper: A new tool to digitally genotype simple sequence repeats
Scienmag
FEBRUARY 4, 2021
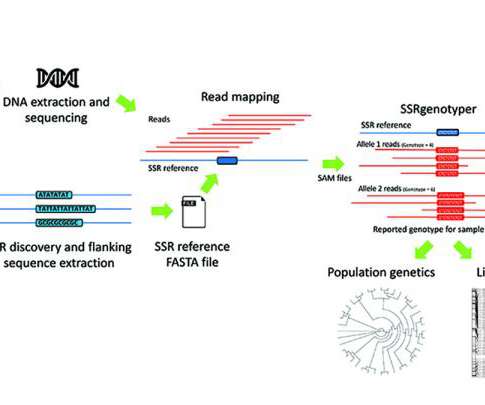
SSRgenotyper: A simple sequence repeat genotyping application for whole-genome resequencing and reduced representational sequencing projects.
Scienmag
FEBRUARY 4, 2021
SSRgenotyper: A simple sequence repeat genotyping application for whole-genome resequencing and reduced representational sequencing projects.

Medical Xpress
JANUARY 5, 2023
National Institutes of Health researchers have published an assessment of 13 studies that took a genotype-first approach to patient care. This approach contrasts with the typical phenotype-first approach to clinical research, which starts with clinical findings.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Scienmag
JANUARY 13, 2021
To discover these associations, researchers need to compare the genomes of many individuals at millions of genetic locations or markers, and therefore require cost-effective genotyping technologies. A new statistical method, developed […].
XTalks
FEBRUARY 4, 2021
The power of leveraging clinical data to decipher disease mechanisms and fuel drug discovery has rapidly grown in the era of genomics and personalized medicine. Generation of strong research dataset cohorts must begin with high-quality clinical samples. Partnerships and Establishing Research Cohorts.

Worldwide Clinical Trials
FEBRUARY 6, 2023
As genome-wide association studies to identify genetic markers for common diseases increase, these questions will surface even more. The best course of action will depend on many variables, such as the disease or population being studied and the genotype/phenotype relationship, risk, and impact on care. Read the full article!
Worldwide Clinical Trials
DECEMBER 12, 2022
genotyping for known variants vs sequencing only vs sequencing and concurrent deletion/duplication analysis), and whether the interpretation of the genetic testing results may have changed over time. What is the difference between a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)-approved laboratory vs a research laboratory?

pharmaphorum
JANUARY 24, 2023
One of the reasons is because researchers now have far more genetic data to work with than was ever previously possible. The cost of testing per human genome in 2006 was approximately $14 million , and in less than two decades, an average consumer-purchased genetic test costs $100.
Let's personalize your content